Climate, environment and space
The JEK2 project is a key measure for accelerating the achievement of the goals of climate neutrality and the decarbonisation of the Slovenian electric power grid, while it also contributes to the reduction of Slovenia’s dependence on imports of fossil fuels.

Low-carbon portfolio
Greenhouse gas emissions over the entire life cycle of JEK2 will be among the lowest relative to other energy sources. This means a contribution to the reduction of CO2 emissions at the national level.
Chart: Comparison of greenhouse gas emissions from the entire energy production life cycle (in grams of CO2 eq/kWh); source: IPCC
COMPARISON OF GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS FROM THE ENTIRE
ENERGY PRODUCTION LIFE CYCLE (IN GRAMS OF CO2 EQ/KWH)
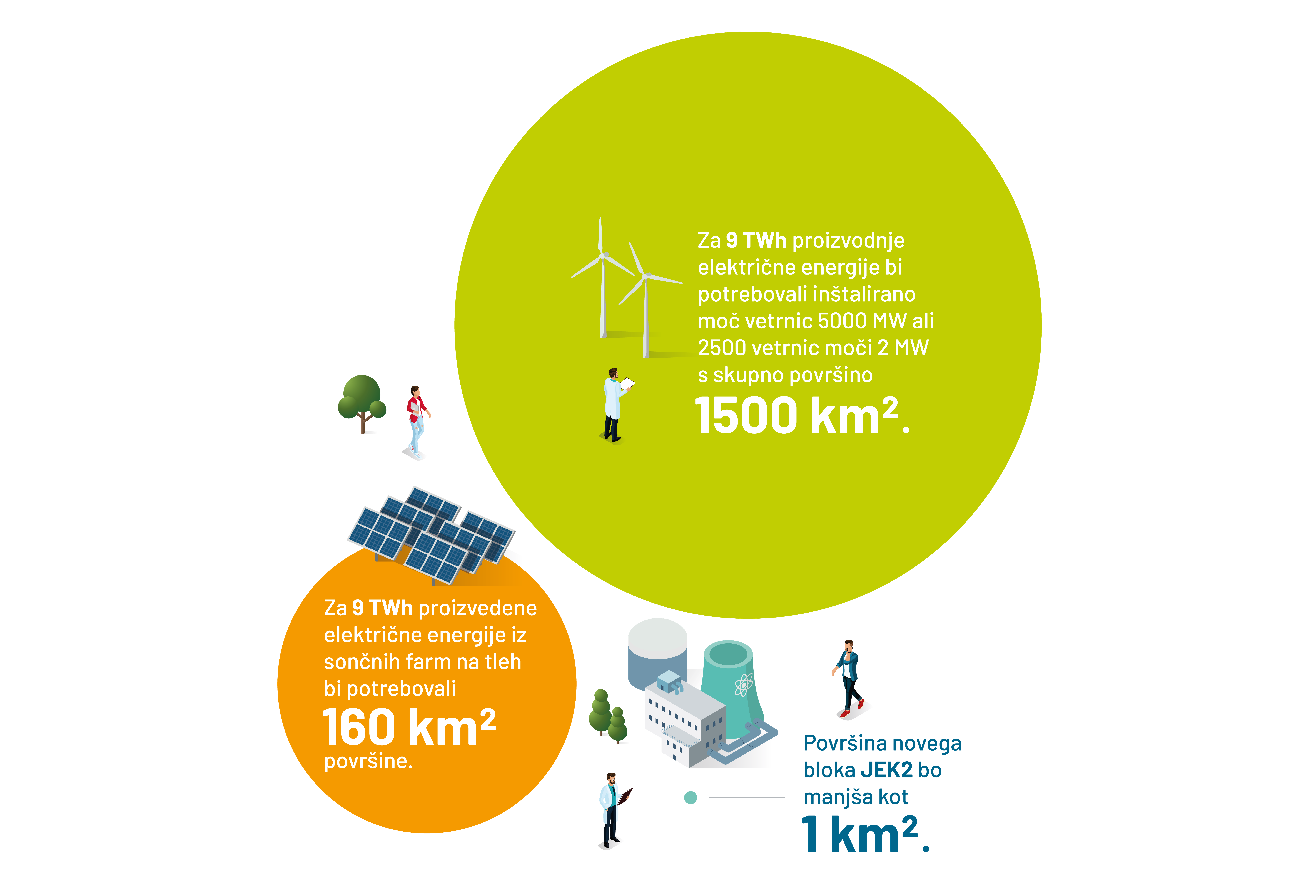
Use of space
The spatial footprint of JEK2 will be minimal in relation to the amount of electricity produced: only 1 km2 of space will be needed to produce 9 TWh of electricity, which a 1,100 MW nuclear power plant would produce annually.
Preservation of biodiversity
The minimal use of space contributes to the preservation of extensive natural areas and their biodiversity.
![European,Bee-eater,,[merops,Apiaster]](https://jek2.gen-energija.si/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/MicrosoftTeams-image-600x399.jpg)
Very low and thus easily manageable quantities of radioactive waste over the entire life cycle
The high energy density of nuclear fuel means that JEK2 will generate little radioactive waste, which be handled carefully and responsibly.
Chart: Average annual quantities of waste per capita in Slovenia; source: ARAO

